【LuoguP1041】【NOIP2003】传染病控制
题目链接: https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1041
前言
这道题正解搜索, 然而可能有一些同学和我一样一开始觉得能用DP做的…推完递推式, 打完DP只有40, 然后也没有找出错误. 我这篇题解主要就来说一下这个DP的思路和错误.
如果你已经懂了DFS思路, 可以理解一下错误DP的思想, 如果看不出错误, 很可能是你对这个题的题意还不够清楚.
分析
先建图, 是以1节点为根的一棵树.
我们开一个一维数组f, 下标代表节点编号. 记录传染到这个点最少再传染给几个人.
我们分类讨论, 先不考虑儿子节点还会继续传染的情况. 如果这个点没有儿子或者只有一个儿子, 那么最少再传染0个人. 否则传染节点数就是儿子数 - 1.
如果儿子节点还会继续传染, 那么我们就切断求出的f值最大的那个.
$$ f[now] = (\sum_i^{i∈sons[now]}f[i] + 1) - (\max_i^{i∈sons[now]}f[i]) - 1 $$
这个式子我实在不会写的更好了, sons代表节点的所有儿子.
看懂的话应该很快就能发现DP的错误在哪.结合这两个说明:
这种疾病的传播有周期性,在一个疾病传播周期之内,传染病将只会感染一代患者,而不会再传播给下一代
以致他们在一个疾病传播周期内,只能设法切断一条传播途径
单独看好像还是找不出这个DP的错误.然后我给出一张图.
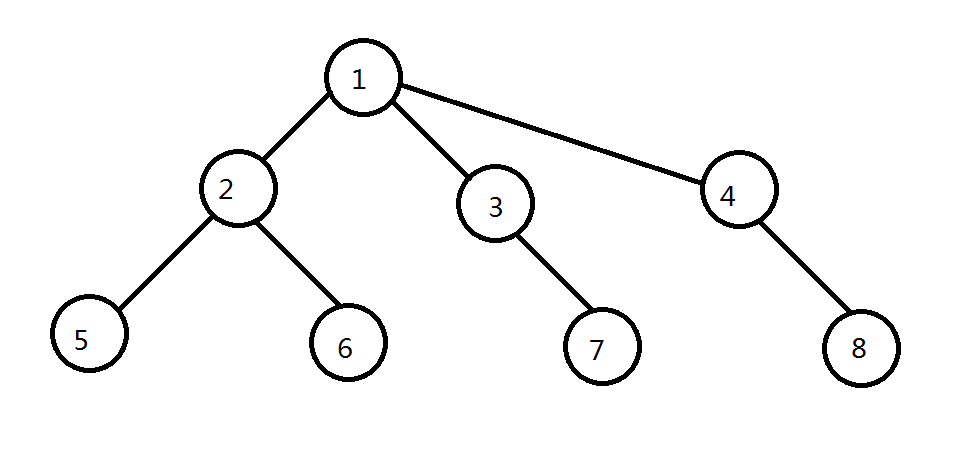
正解应该是4, 然后DP竟跑出更优解3…其实是因为他在同一个疾病传播周期内切断了两条.DP将会先切断2, 然后切断7和8. 然而7和8在同一个传播周期内, 所以不能同时切断.
这就是DP的错误, 不符合题目要求. 然后就只能考虑搜索, 因为DP的启发, 就很容易想到按深度来搜索了.
代码
错误DP代码(40分):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| #include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int n, p, sums, f[301], head[301], edptr= 1;
int tmpx, tmpy;
struct edge {
int to, nexty;
} eds[1001];
void add(int a, int b) {
eds[edptr].to= b, eds[edptr].nexty= head[a];
head[a]= edptr++;
return;
}
void dp(int nown, int fa) {
int sons= 0, maxs= 0, tot= 0;
for(int i= head[nown], to; i; i= eds[i].nexty) {
to= eds[i].to;
if(to == fa) continue;
dp(to, nown);
++sons, maxs= max(maxs, f[to]), tot+= f[to];
}
if(sons >= 2) f[nown]= tot - maxs + sons - 1;
return;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> p;
for(int i= 0; i < p; i++) {
cin >> tmpx >> tmpy;
add(tmpx, tmpy), add(tmpy, tmpx);
}
dp(1, -1);
cout << f[1] + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
|
正解搜索代码(100分):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| #include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, p, head[301], edptr= 1;
int tmpx, tmpy;
struct edge {
int to, nexty;
} eds[1001];
void add(int a, int b) {
eds[edptr].to= b, eds[edptr].nexty= head[a];
head[a]= edptr++;
return;
}
int dep[301], f[301], cutd[301];
vector< int > node[302];
void cut(int nown, int s) {
cutd[nown]= s;
for(int i= head[nown], to; i; i= eds[i].nexty) {
to= eds[i].to;
if(to != f[nown]) cut(to, s);
}
return;
}
void dfs1(int nown, int fa) {
dep[nown]= dep[fa] + 1, f[nown]= fa;
node[dep[nown]].push_back(nown);
for(int i= head[nown], to; i; i= eds[i].nexty) {
to= eds[i].to;
if(to != fa) dfs1(to, nown);
}
return;
}
int ans= 0x3f3f3f3f;
void dfs2(int deep, int cost) {
if(cost >= ans) return;
int notsolve= 0;
for(int i= 0; i < (int)node[deep].size(); i++)
if(!cutd[node[deep][i]]) ++notsolve;
if(!notsolve) {
ans= cost;
return;
}
for(int i= 0; i < (int)node[deep].size(); i++) {
if(cutd[node[deep][i]]) continue;
cut(node[deep][i], 1);
dfs2(deep + 1, cost + notsolve - 1);
cut(node[deep][i], 0);
}
return;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> p;
for(int i= 0; i < p; i++) {
cin >> tmpx >> tmpy;
add(tmpx, tmpy), add(tmpy, tmpx);
}
dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(2, 1);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
|

